|
| Alzheimer’s Disease Patient |
Overview of Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder which is associated with a progressive loss of structure and function of neurones that leads to neuronal death.
The neurodegenerative disorder results in impairment of the person’s memory and ability to perform daily activities The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. The disease causes deterioration in memory, thinking, behaviour and the ability to perform everyday activities.
Briefly to say Alzheimer's disease is a most common form of dementia and it may contribute 60-70% cases of dementia.
Alzheimer's disease is becoming a major health issue in the world. It us an ever-increasing challenge as the population ages and life expectancy increases.
The statistical data are alarming, with an average of one person losing memory due to Alzheimer's disease every three seconds in the world. In the past years only had Alzheimer's disease but these days young and middle aged people are also victims of the disease.
Alzheimer's disease and related dementias have affected over 50 million persons worldwide.
Statistical data shows that the number of persons with Alzheimer's disease has been increasing and it is estimated that the number of people suffering from this disease will increase by 70 million by 2030.
Alzheimer's disease at a glance:
 |
| Alzheimer’s Disease at glance |
What is Alzheimer's disease?
Alzheimer's disease is a brain killer which kills brain cells causing deterioration in memory,thinking, behaviour and the ability to perform everyday activities. It is also called neurodegenerative disease as it is a brain related problem. This disease causes constant damage to the brain cells. The disease presents with varying combinations of progressive cognitive, emotional, motor, autonomic, and peripheral symptoms and clinical signs. Loss of memory is devastating.
Causes of Alzheimer's
Disease
Data shows that age is the most important overall risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease is 0.5 % at the age of 60 and it is 40% at the age of 90.
Thus age increases a person's risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. Similarly, data says that nearly 70 percent of Alzheimer's diseases are caused by heredity. Thus genetic factor main factors for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, high blood pressure, head injuries, obesity, etc. can also cause Alzheimer's disease.
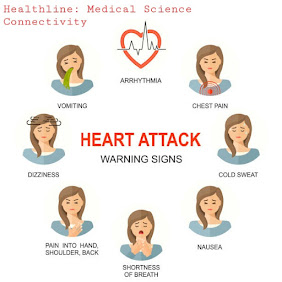
Sign and symptoms connected to Alzheimer's disease
The sign and symptoms linked to Alzheimer's disease are :
- Impairment of episodic memory in which patients forget recently completed activities or events.
- Decreased ability to think .
- Difficult in speaking and repeat same words many times.
- As the disease becomes severe, person cannot recognize people around him/her.
- At severe stage person loses the ability to do every day task.
Note that the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease worsen over time.
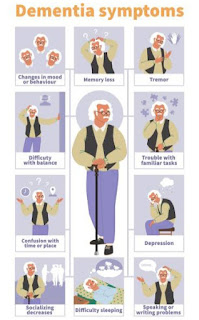 |
| Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease |
Stages of Alzheimer's disease
The different stages of Alzheimer’s disease are summaries of the changes in abilities typically seen in persons with the disease.
Usually Alzheimer's disease starts silently and slowly, with the change in structure and function of neurones that begins years before anyone notices a disorder in a person.
On the basis of the changes in abilities typically seen in persons with the disease, main stages of disease have been described as:
1. Early or Preclinical Stage AD
During this stage the changes in structure and function of neurones due to Alzheimer’s disease are happening slowly but the patients is not showing signs of disorders. During this stage persons with Alzheimer's disease function at high level, so it cannot be diagnosed. This stage can last for years or decades. At this stage brain imaging shows deposits amyloid protein in the brain. This deposits of amyloid protein interferes with the brain's communication system.
2. Mild Stage of AD
During this stage , signs and symptoms connected to Alzheimer's disease begin to be noticeable. Person with mild Alzheimer’s disease:
- Forgets recently happened or informed events, places, names or informations
- Feels difficulty in finding right words to speak.
- Has confusion about time and place
- Repeats the same questions over and over
- Has difficulty in solving problems
- Takes longer to time to complete normal daily activities
- Feels difficulty in completing complicated tasks such as managing money and paying bills
- Loses or misplaces the object
- Experiences chane in personality
Most of person with mild Alzheimer’s disease have no problem recognizing familiar faces and can usually travel to familiar places
3. Moderate Stage of AD
During this stage, person with AD require assistance. Person with AD in this stage:
- Has increased memory loss and confusion. Often forgets events or details about his/her own life
- Feels some difficulty in recognizing friends and family members
- Has difficulty in carrying out multi-step tasks.
- May need some help with self-care ,such as bathing, showering and toileting
- May need help choosing proper dress and may need help putting clothes in right place
- Experiences more changes in personality including being agitated ,acting out
- Wanders from his/her living place
4. Moderately Severe Stage of AD
During this stage, person with moderately severe AD :
- Has significant confusion in recognizing his or children or spouse or other family members.
- Loses skills in dressing, bathing and toileting
5. Severe Stage of AD
During this severe stage, person with AD :
- Has almost total memory loss
- Needs help with all basic daily activities
- Completely unaware of his or her surroundings
- Begins a decline in ability to sit up,walk and eat without assistance
6. Very Severe Stage of AD
During very severe stage of disease, the person:
- Loses the ability to communicate. Speech becomes limited to a few words .
- Loses the ability to control bladder and bowel function.
Management of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and prognosis of Disorders
The management of a patient with Alzheimer’s disease involves many
sensitive issues. It is very important humanitarian job to provide medical and psychological support to patients as well as to their families and carers. During the
progression of the disease there will be different goals at different stages, ranging from aiding failing cognitive function in the setting of independent living, to managing behavioural problems and aggression, and eventually to providing full supportive nursing care.
There is great variation in the rate of progression, but depending on
the age and stage of disease at diagnosis, on average, patients spend several years in the mild or minimal stages (although it can be as long as 5–10 years), between 4 and 5 years in the moderate disease stages, and, depending on the quality of care in the dependent stages, a year or more requiring full nursing care.
Nonpharmacological treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
The mainstay of treatment is social support and increasing assistance with day-to-day activities. Depending on individual circumstances, symptoms, and disease stage, there may be different requirements for the support . All these supports are nonpharmacological treatment.
Nonpharmacological treatment or support includes:
• information and education
• diet, exercise, mental activity
• carer support groups
• community dementia team, including home nursing and personal care
• community services (e.g. meals-on-wheels, community transport services)
• access to dementia charities
• sitter service
• day centre
• respite care
• residential/nursing home
• palliative care
How to avoid Alzheimer's disease
There is no definitive way to prevent Alzheimer's disease. Scientists are still researching it. However, the risk of Alzheimer's can be reduced by controlling the risk of heart disease, cholesterol, obesity and diabetes. In addition, regular exercise from a young age can reduce the risk of Alzheimer's.